Procedure 4: Create a Date with a specific Date and Time format
Dates have rather special treatment in R, not least that data can be presented in raw data in a variety of formats (e.g. DDMMYYYY, DD/MM/YYYY). The date data type in R exists for the purpose of interacting and manipulating dates.
A vector of dates would start out as a character vector:
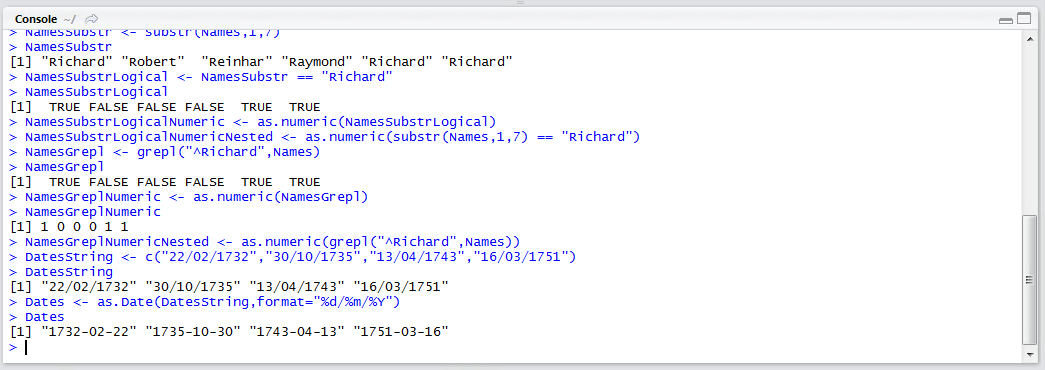
DatesString <- c("22/02/1732","30/10/1735","13/04/1743","16/03/1751")
Run the line of script to console:
It can be observed that the dates are of the form charterer by typing:
Run the line of script to console:

To convert the DatesString vector to the correct data type, R needs to know where to find the year component, the day component and the month component while knowing how to separate the elements. The following tokens specify the components:
- %Y is a four digit number.
- %y is a two digit number.
- %m is the month as a number.
- %d is the day as a number.
- %b is a short month (such as Jan).
- %B is a long month (such as January).
Outside of the % tokenisation characters can be specified that should be excluded in the overall tokenisation. To convert the character string vector of dates to a date vector type:
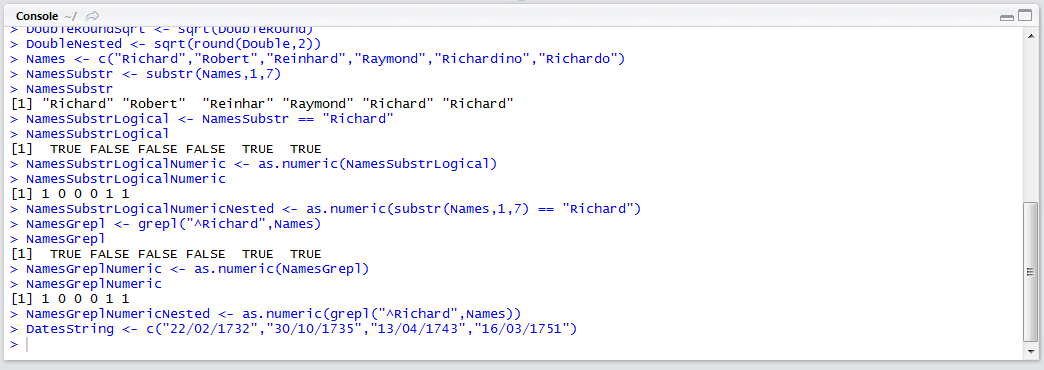
Dates <- as.Date(DatesString,format="%d/%m/%Y")
Run the line of script to console:
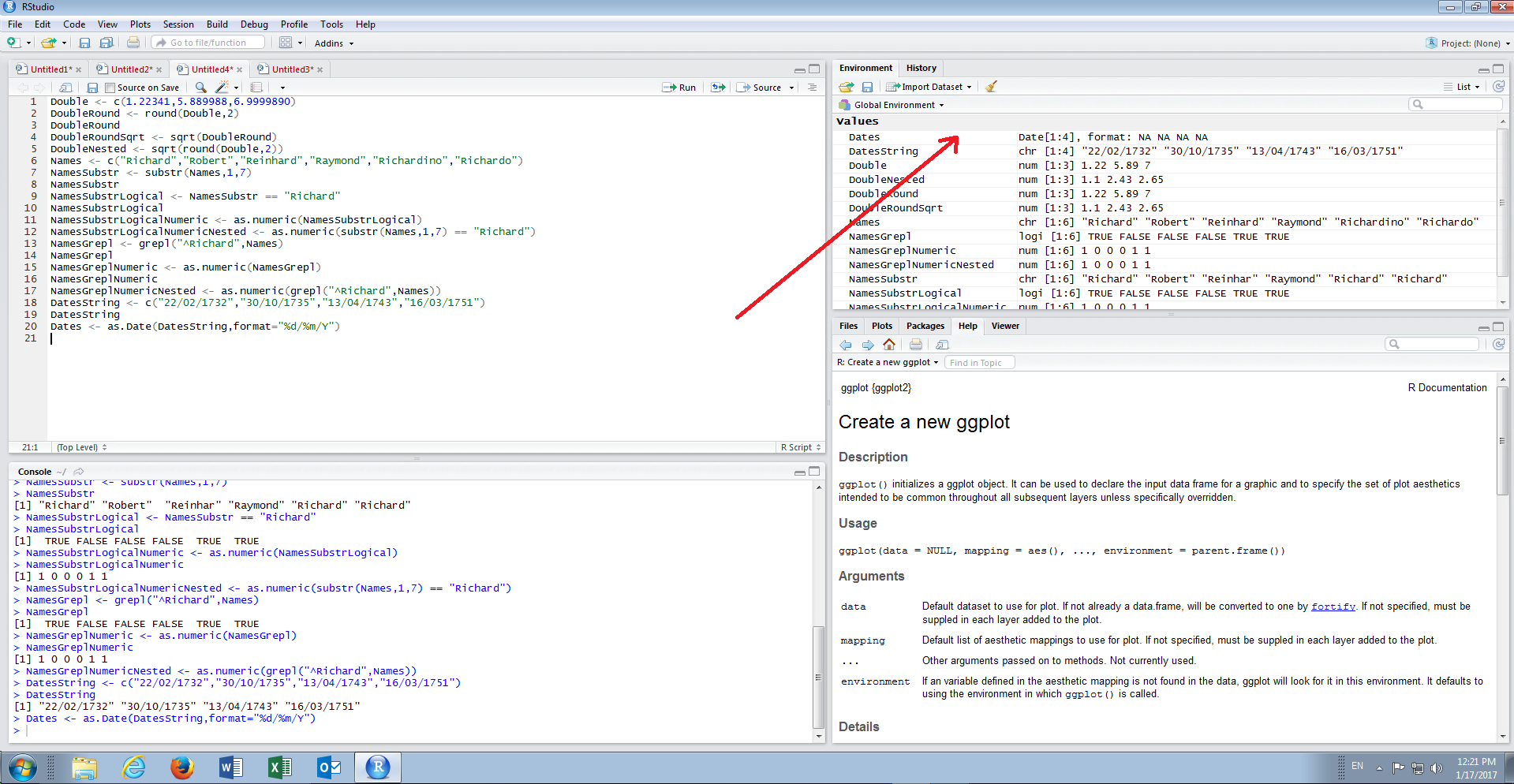
It can be observed that the Dates vector has been created in the environment pane:
Run the line of script to console: